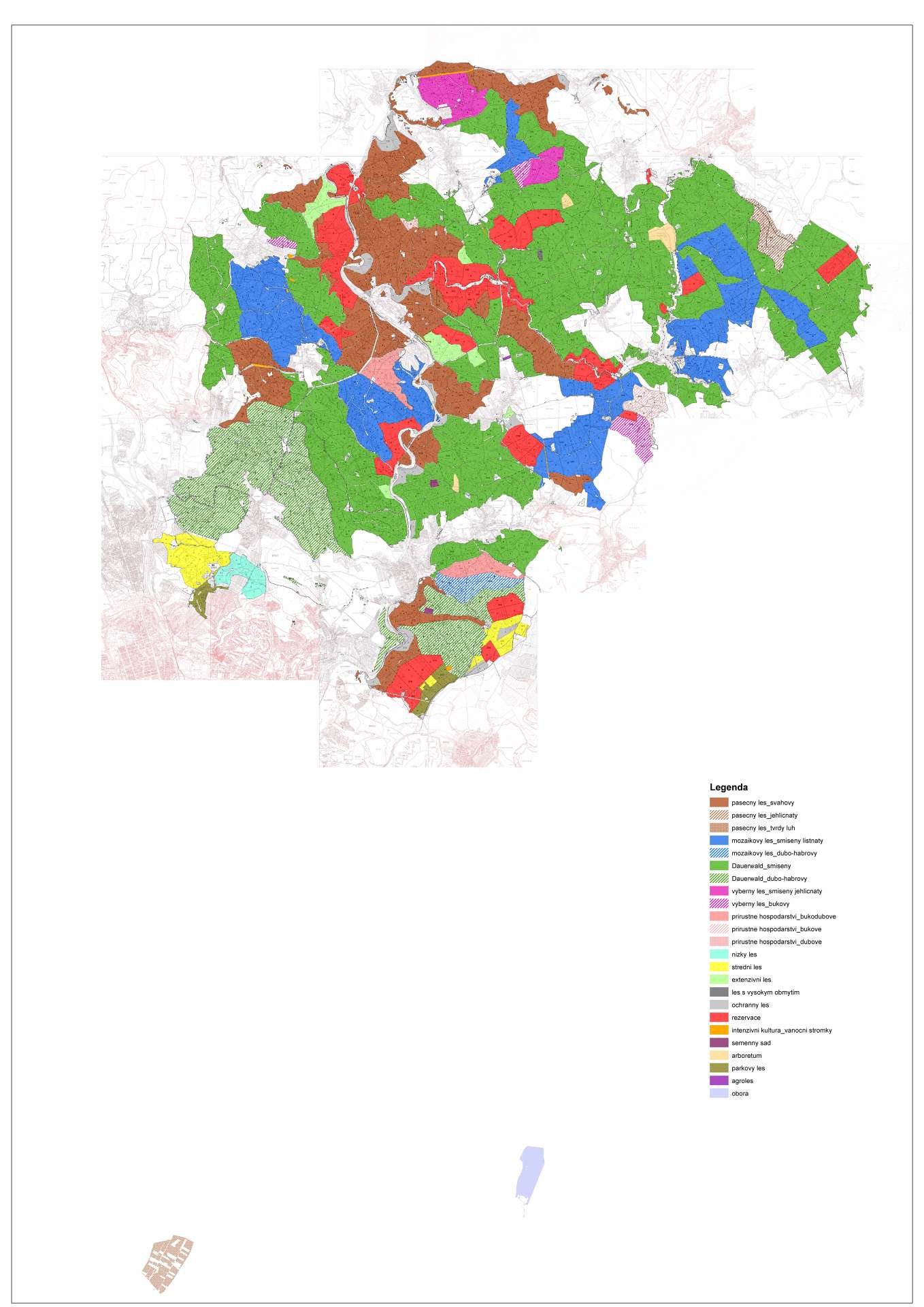
Management concept
Our forest management concept “Diverse forests for climate change”
aims at:
- increasing the resilience of forests by introducing appropriate adaptive and mitigation management measures under changing environmental conditions
- optimal use of the production potential of forests with regard to habitat conditions
- ensuring the fulfilment of forest ecosystem services and other functions, with particular regard to the needs of the university (teaching, research) and the public (recreation)
based on
- the latest trends in forestry, scientifically based and practically tested – in accordance with the principles of the pan-European Pro Silva movement (the Czech branch of Pro Silva Bohemica was founded in 1995 at MENDELU Brno with the first excursion to UFE)
- comprehensive strategic documents of the Faculty of Forestry and Wood Technology in Brno – see for example Čermák, P., et al. (2016): Catalogue of forestry adaptation measures.
- the purpose-oriented mission of UFE – i.e. operational implementation, verification and presentation of timeless methods and economic approaches
is realized:
- on the whole area of UFE according to actual natural conditions
- using 10 key management principles or adaption measures
- cultivation of diverse forests – diversity in species, age and space
- small area management with the application of selective principles, continuity of stand cover and standing volume – with a view to optimising volume growth and forest stability
- exploiting the creative forces of nature, in particular natural forest regeneration and self-selection
- stand education – mainly individual positive, oriented to the quality of production
- use of suitable adaptable geographically non-native tree species
- formation and maintenance of the vegetation cover
- minimising the negative impact of game on the forest
- implementation of biotechnical measures for water retention in forests
- general promotion of biodiversity, including through habitat trees and deadwood
- proper partitioning for harmless approach of timber and to facilitate game hunting
- through 16 economic models in which the above measures are incorporated to varying degrees
- Dauerwald: mixed non-stationary forest with implementation of individual and group selection – freestyle, predominant function – production (the model is predominant in area, classified forest stands are mostly in the initial phase of conversion)
- Mosaic forest: mixed small-area forest with implementation of group mowing and small-area undergrowth elements, predominant function – production
- Selective forest: distinctly non-coniferous forest (coniferous or beech type) with implementation of individual selection, predominant function – production
- Forest managed under systems involving coupes: mixed old-growth forest with undergrowth and emergent forms (mainly in sloping terrain and floodplain forest), predominant function – production
- Incremental forest management: a form of the passive model consisting of strong release drills, the predominant function is production
- Low forest: clear-felling type (incl. exhibition form), predominant function – production
- Coppice-with-standards: strong release clearing and a specific form of screen cutting, predominant function – production
- Extensive forest: less intensive logging activity (health, or maturity selection), no cultivation activity, predominant function – biodiversity
- High-growth forest: health selection, prevailing functions are realized – demonstration
- Protective forest: individual selection of low intensity, predominant function – protective
- Reserves: no-management areas, predominant function – biodiversity
- Seed orchard: predominant function – source of reproductive material
- Arboretum: predominant function – study and recreation
- Park forest: predominant function – recreational
- Agroforest: strips of trees with shrubs and agricultural crops in between on forest and agricultural land, predominant function – production
- Game preserve: predominant function – game farming